INJECTION MOLDING
Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce plastic parts by injecting molten plastic material into a mold. It’s ideal for producing high volumes of identical parts with precision, efficiency, and consistency. It’s commonly used in industries like automotive, consumer products, packaging, medical devices, and electronics.
Advantages of Injection Molding
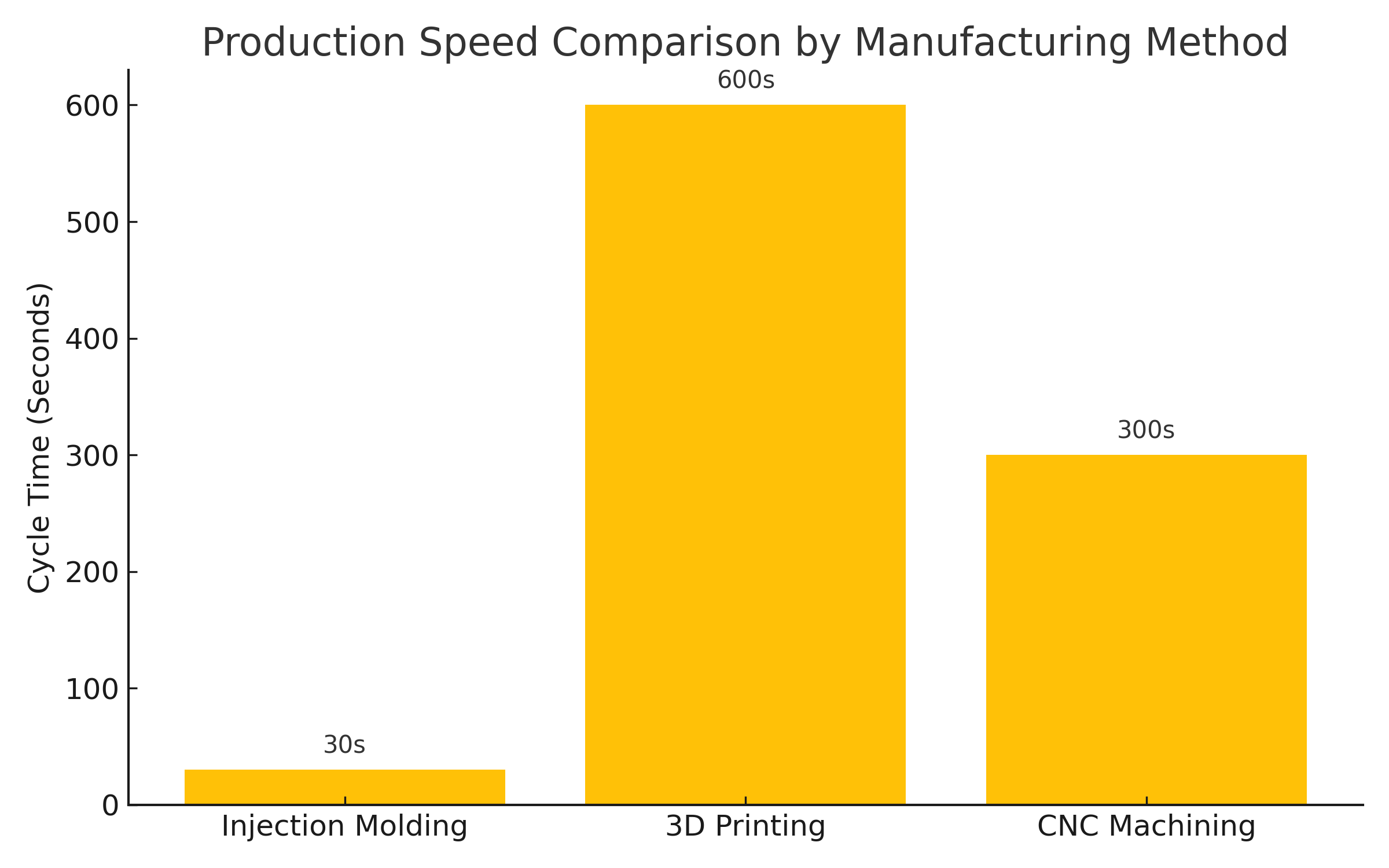
- High efficiency for large volumes: Once tooling is made, parts can be produced quickly and consistently.
- Low unit cost at scale: Ideal for high-volume production runs.
- Excellent surface finish & detail: Can produce parts with smooth surfaces and intricate features.
- Minimal material waste: Excess plastic can often be reground and reused.
- Supports multi-material options: Co-injection or overmolding allows combining different materials or colors.
- Automation friendly: Highly suitable for robotic and automated production systems.

The Process:
- Clamping: Mold halves are securely closed.
- Injection: Melted plastic is injected into the mold cavity under pressure.
- Cooling: Plastic cools and solidifies within the mold.
- Ejection: The mold opens, and the part is ejected.
Decision Drivers
- Part Size
- Typically used for small to medium-sized parts.
- Part Complexity & Geometry
- Ideal for highly detailed parts, complex geometries, tight tolerances, internal features, undercuts (with side-actions).
- Surface Finish & Aesthetics
- Ideal for consumer products or parts requiring visual appeal without post-processing.
- Production Volume
- High-volume production justifies the high tooling cost – Economies of scale kick in at thousands to millions of parts
- Tooling Costs & Lead Time
- Tooling is expensive and time-consuming; steel molds can cost tens of thousands of dollars and take weeks to months to manufacture.
 CONSIDER
CONSIDER